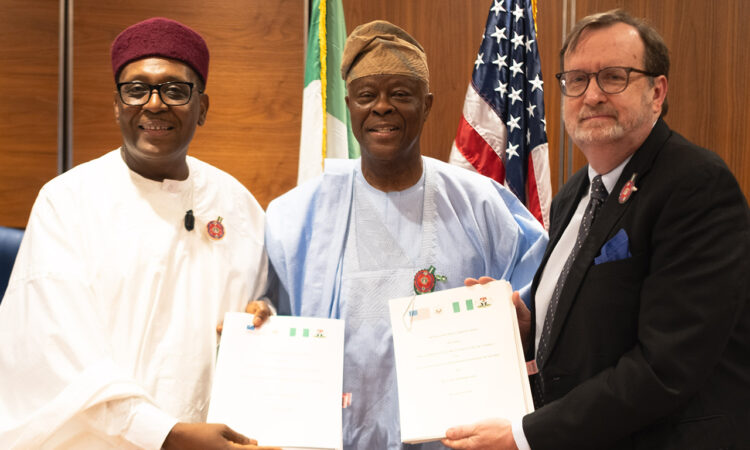

In a major development for Nigeria’s healthcare sector, a $2.1 billion health grant has been approved by the United States. The funding forms part of a five-year agreement between both countries and is aimed at strengthening healthcare delivery nationwide.
Importantly, special attention has been placed on faith-based healthcare facilities, which continue to serve millions of Nigerians, especially in rural and underserved communities.
US–Nigeria Health Partnership Explained
This collaboration falls under the America First Global Health Strategy. As a result, a renewed approach to bilateral health cooperation between Washington and Abuja has been introduced.
According to official reports, the agreement is expected to improve access to essential healthcare services while strengthening Nigeria’s overall health system.
What the Funding Includes
Under the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed by both governments, long-term financial commitments have been outlined.
- The United States will contribute nearly $2.1 billion over five years.
- Nigeria has pledged to increase domestic health spending by almost $3 billion.
This makes the agreement the largest co-investment under the strategy so far. More details can be found via BusinessDay Nigeria .
Key Health Areas Covered
The funding is expected to support several essential healthcare services, including:
- Prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and polio
- Improved maternal and child healthcare services
- Strengthening of healthcare systems nationwide
- Expanded support for faith-based health institutions
Focus on Faith-Based Healthcare Facilities
Faith-based clinics and hospitals play a vital role in Nigeria’s health system. It is estimated that these facilities serve over 30 percent of the population, particularly in areas with limited public healthcare services.
Although faith-oriented, medical care is provided to all Nigerians regardless of religion. Services such as immunisation, maternal care, and infectious disease treatment are widely offered.
You can read more about Nigeria’s health system on our General News section.

Why This Development Matters
Nigeria continues to face serious healthcare challenges. High maternal and child mortality rates remain a concern, while infectious diseases such as malaria and tuberculosis persist.
Therefore, strengthening healthcare systems has been identified as a critical step. Experts believe the partnership could improve access to care and enhance disease prevention.
Expected Benefits
- Improved healthcare access for vulnerable populations
- Support for government-run health services
- Increased local capacity and workforce development
- Expanded preventive care and early disease detection
Nigeria’s Commitment to the Agreement
As part of the agreement, Nigeria has committed to increasing domestic health financing. Priority will be given to interventions that directly benefit communities nationwide.
This shared responsibility is expected to support long-term sustainability beyond foreign aid.
Conditions and Ongoing Reviews
US officials have stated that foreign assistance funds remain subject to periodic review. Continuation of support may depend on progress in policy alignment and governance priorities.
Conclusion
Overall, the $2.1 billion grant represents a significant boost for Nigeria’s healthcare sector. By strengthening faith-based healthcare services, millions of Nigerians may gain better access to essential medical care.
Through continued cooperation, improved health outcomes are expected, particularly for mothers and children across the country.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, financial, or legal advice.








No Comments